Written by Lucas
1. Overview:
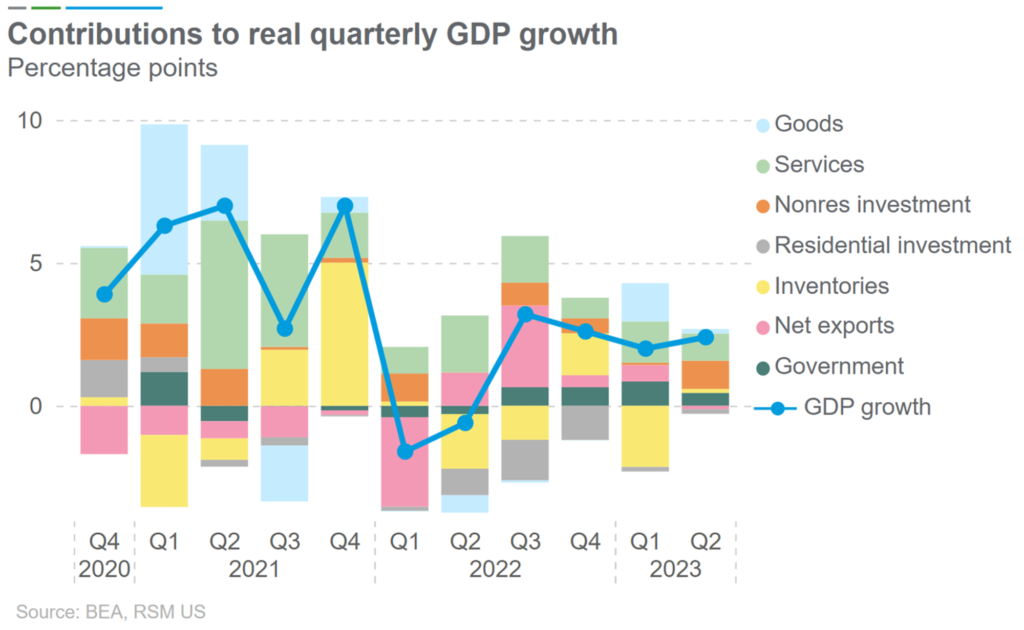
- The GDP in Q2 has increased at an annual rate of 2.4%, predominantly driven by the growth in consumer spending and business investment. On the other hand, as described in the chart below, the economy in the United States has exhibited a comparatively slower pace than the corresponding period in the previous year, albeit remaining distant from a state of recession.
- The inflation rate in June, as measured by Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) excluding seasonal factors, has decreased to 3%, marking the lowest level since March 2021.
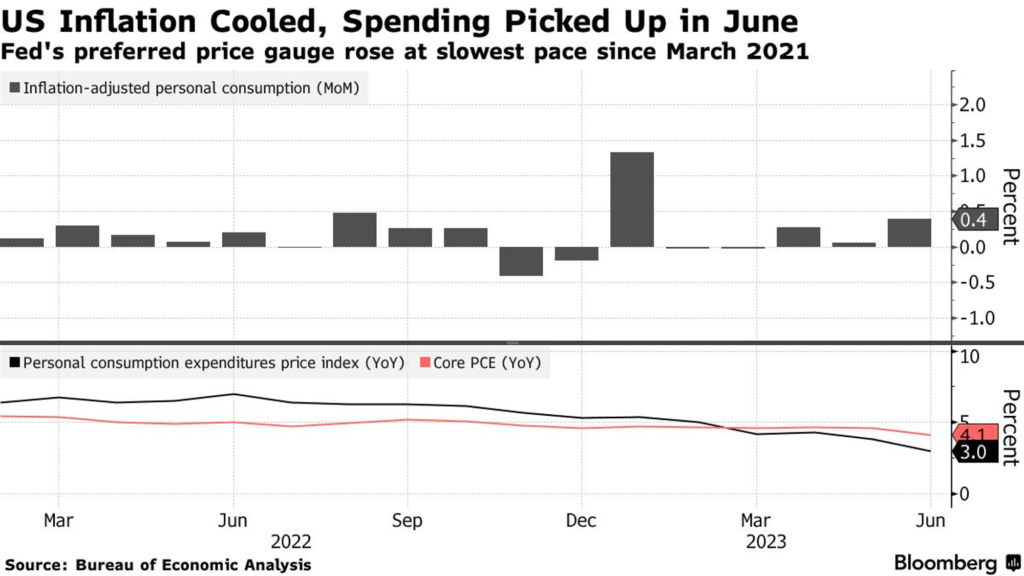
- Although the overall inflation has decreased to 3%, the core PCE index, which is the policy-determined measure by the FOMC, remains above 4%—twice the targeted level. The persistently high inflation is primarily driven by the sustained purchasing power of consumers, as wage growth for American workers has exceeded expectations in the previous month.
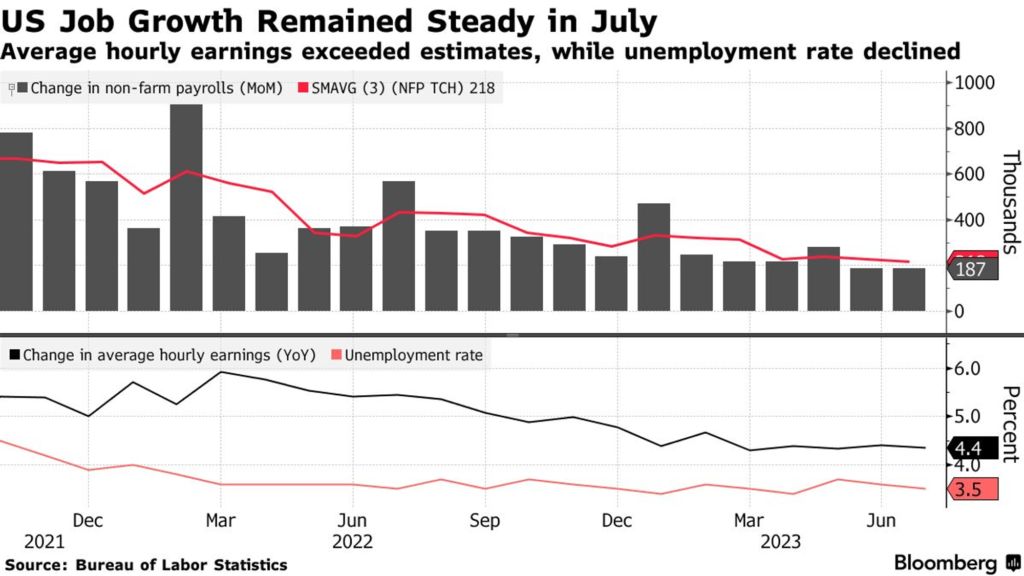
- Therefore, the FED has raised interest rates to a range of 5.25%-5.5%, reaching the highest level in over 22 years. Particularly, Chairman Powell and his colleagues maintain a neutral stance regarding the future policy direction, refraining from definitively affirming an additional 0.25bps interest rate hike in September, as it relies on the two CPI indicators and the two unemployment indicators.
2. What Does This Mean For The Markets?
- The key takeaway here is that inflation is expected to take longer to cool down, thus the FED will likely maintain higher interest rates for a longer period of time. There are two scenarios:
- One scenario is that the Federal Reserve decides to pause interest rate hikes, which would send a positive signal to the global economy by boosting optimism among individuals and businesses. This, in turn, could lead to increased investment and spending, reducing the likelihood of a recession. Currently, there is a high forecasted probability (68%) of the US economy entering a recession within the next 12 months.
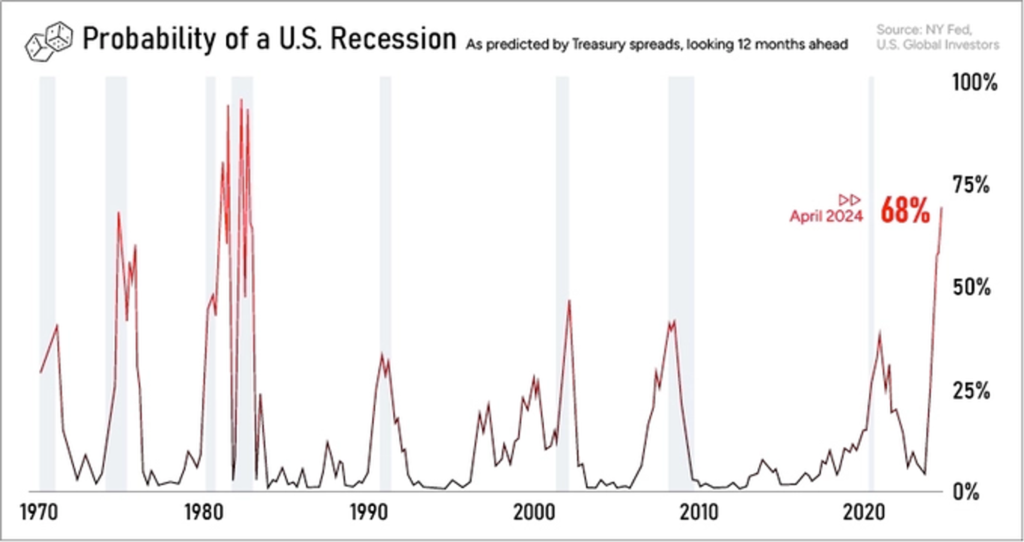
A recession has the potential to significantly alter the income prospects of companies. Goldman Sachs has predicted that the S&P 500 index could decline to 3400 points.
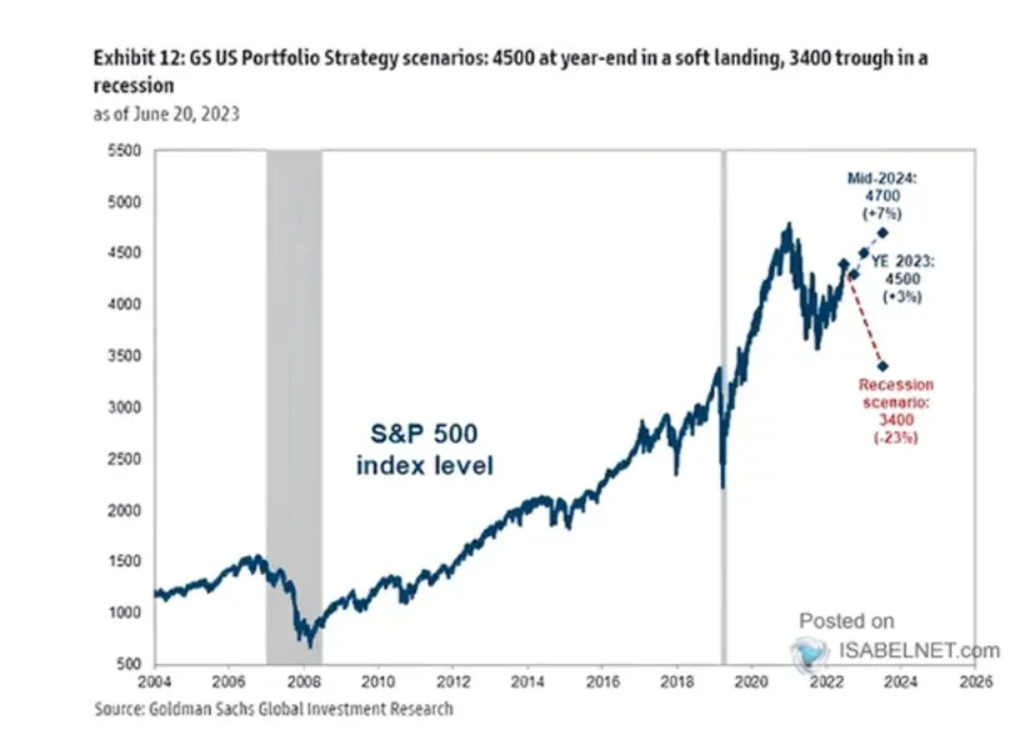
- The second scenario is that the FED continues to raise interest rates. In this case, the risks are likely to increase due to higher borrowing costs, which would result in lower levels of investment and slower economic growth. This, in turn, raises the possibility of a recession and creates the potential for disruption in financial markets.
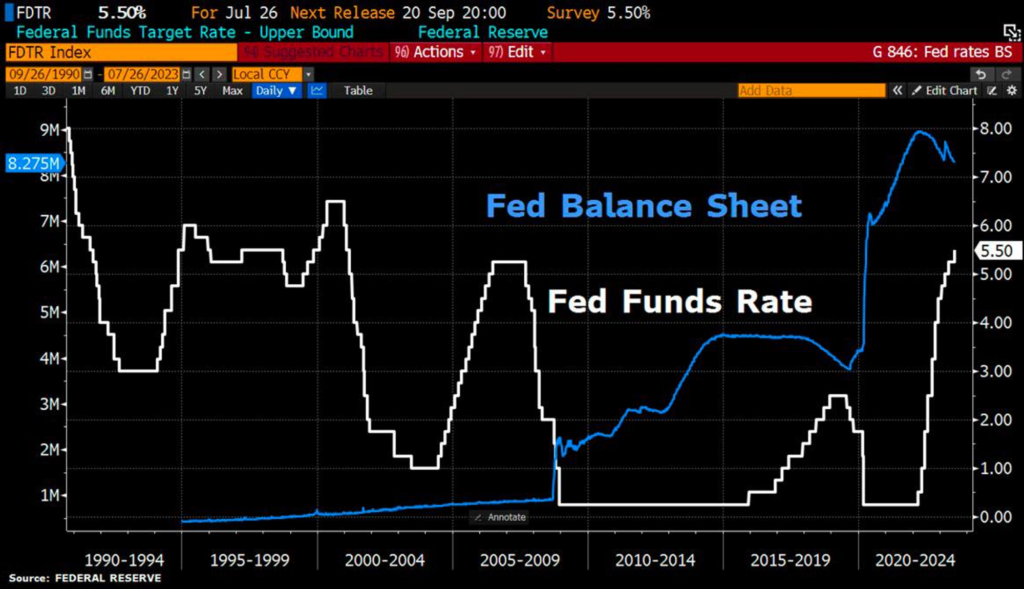
- Furthermore, in the current context where the Fed Fund Rate has reached its peak, the Federal Reserve will continue to reduce its bond holdings on the balance sheet, which currently stands at $8.2 trillion, at a pace of $95 billion per month. This signifies a continued decrease in the money supply available in the market.
- A significant amount of liquidity will be withdrawn as both the FED and banks are projected to pull back more than $1.2 trillion by the end of the year, according to Bloomberg. While individuals continue to deposit money into the currency market, liquidity will gradually diminish. As a result, the financial market will experience increased volatility. However, the impact may not be excessively negative because, despite the withdrawal of over a trillion in reserves, there is still a defensive cash position of $5.5 trillion yielding over 5%.
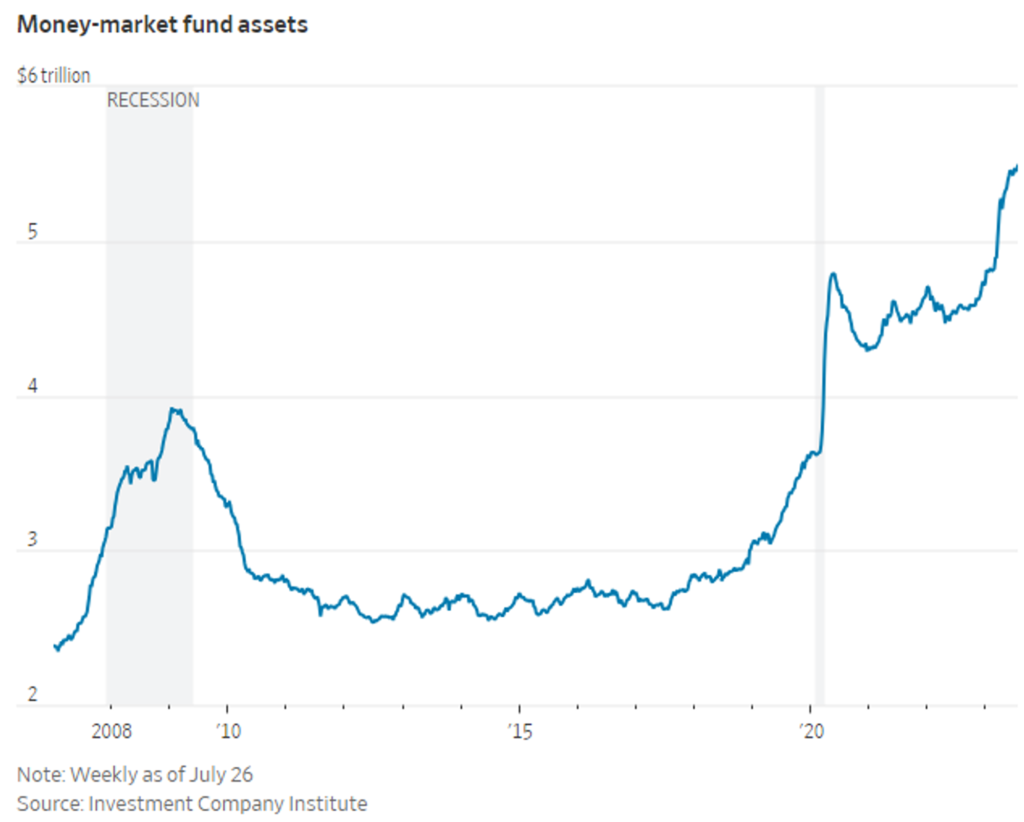
- Currently, the market’s optimism regarding a soft-landing scenario, coupled with increasing cash holdings by investment funds and continuous inflows of retail money, are short-term factors supporting the market:
- The cash allocation of FMS has increased to 5.3% from 5.1%. Institutional investors remain pessimistic about the economy due to concerns that the market expectations are overly optimistic, thus posing higher risks.
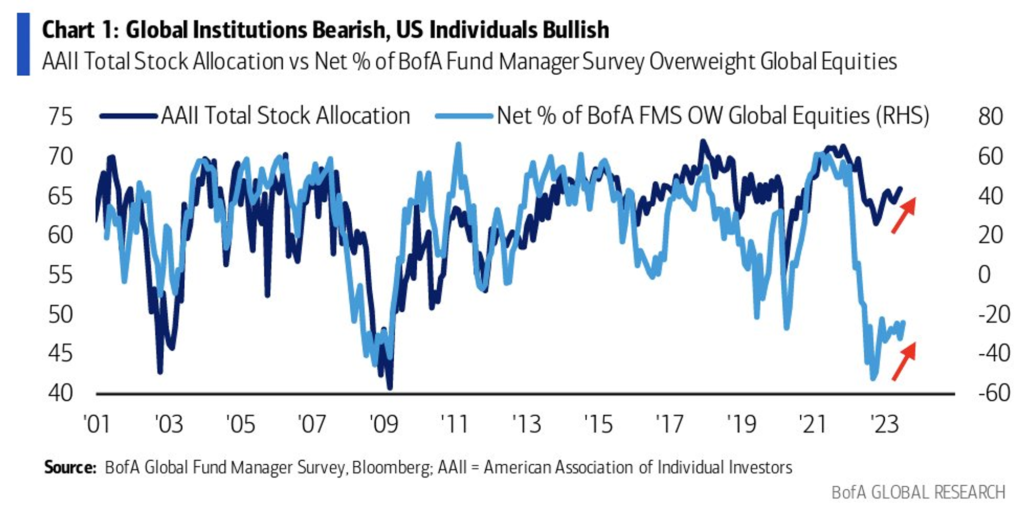
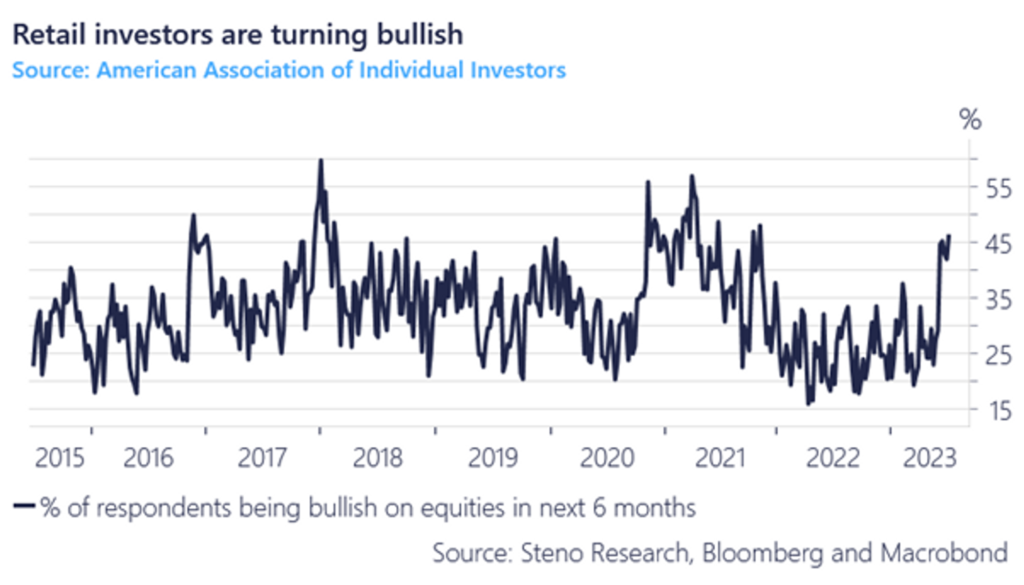
- On the other hand, individual investors are currently displaying a high level of optimism, which is a significant departure from the negative sentiment experienced since late 2021. They are consistently pouring money into the stock market.
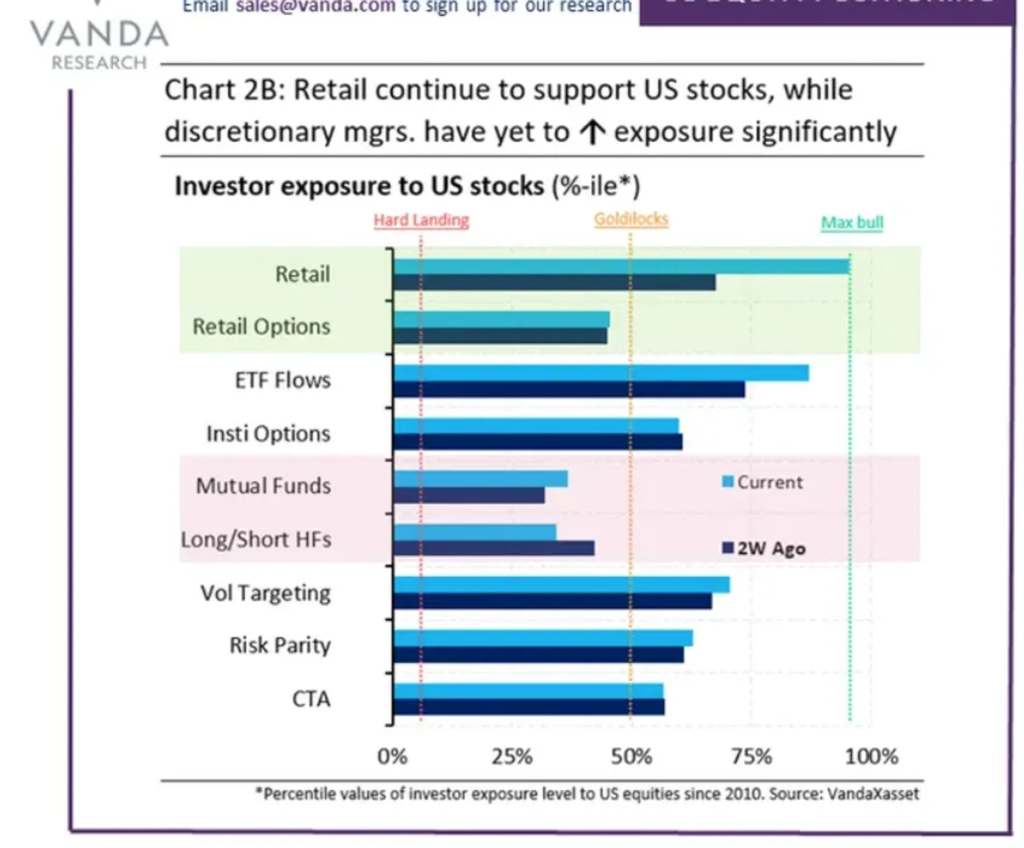
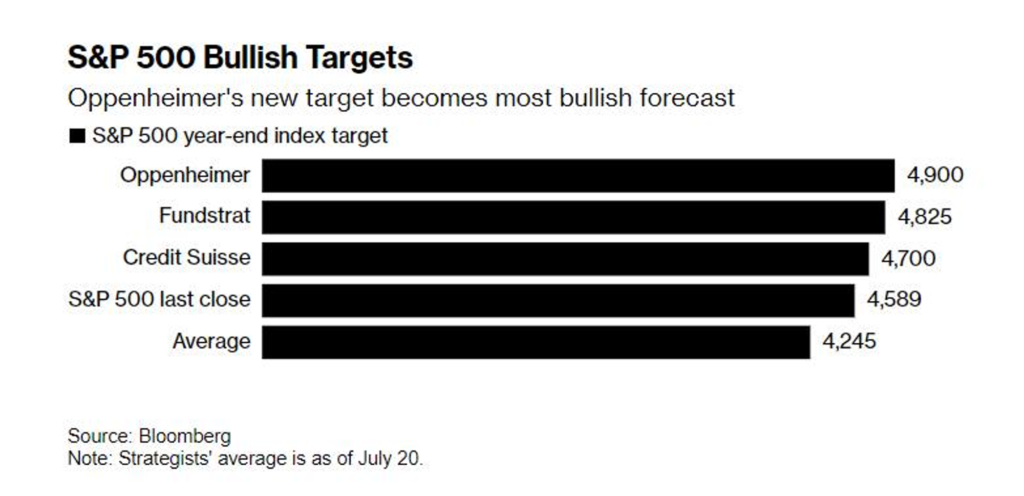
- There are long-term concerns due to the current risk-free rate being around 5%. Investors expect stocks to generate returns higher than this rate. However, the growth targets set by major investors indicate that the most optimistic scenario for the S&P 500 would only result in a 10% increase. This suggests that there is limited potential for significant growth in the last four months of the year.
3. Conclusion and Action Plan:
- In the short term, the US economy has not yet entered a recession, with higher-than-expected GDP growth, a low unemployment rate (3.5%), and a continued downward trend in inflation. However, when monetary policy fully permeates the economy, it may weaken, and in the medium term, this will be reflected in the stock market.
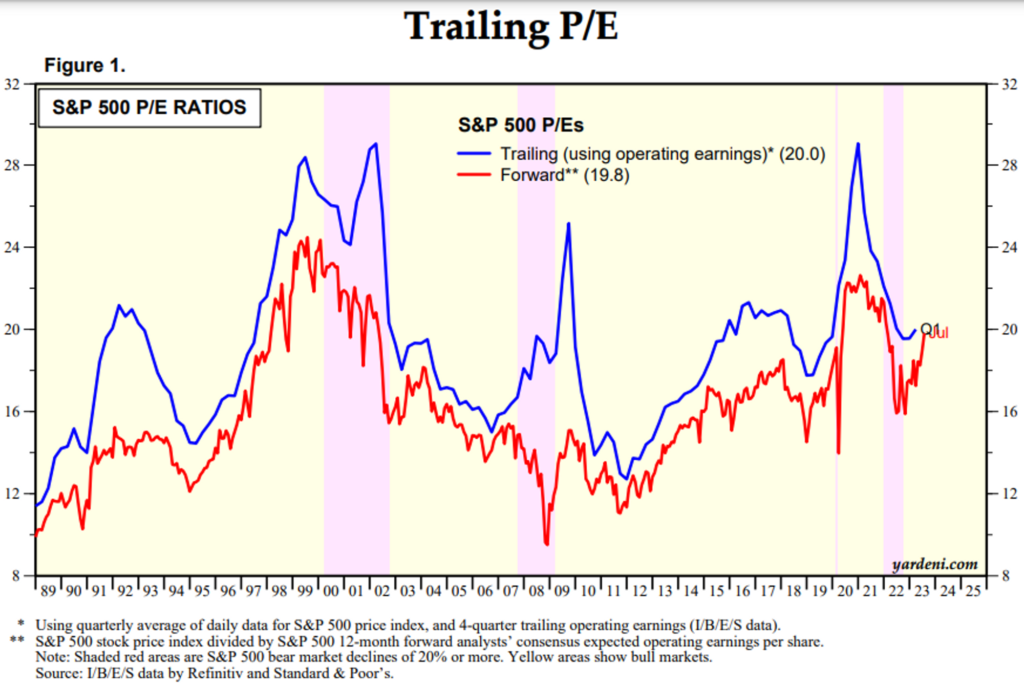
- If interest rates rise rapidly and strongly to 5% or higher, and if they maintain this high level for the next six months, there will still be many “slow-burning bombs” ahead. The current market has not fully priced in the prolonged effects of QT, and once a significant amount of money is withdrawn, retail investors’ funds entering the market will weaken, and the optimism about an economic recovery may be driven in a different direction. In such a scenario, the probability of the market reversing and experiencing a decline is high. Especially, the S&P 500 is currently trading at a multiple of 20 times earnings, which is relatively high compared to the long-term average of 15.6 times earnings.
- Advice: Exercise caution and increase defensive measures.