1. Overview
Bitcoin, the largest blockchain in terms of market capitalization, has not yet achieved a significant DeFi ecosystem like Ethereum. Despite having the necessary tools and infrastructure, Bitcoin’s DeFi progress still falls behind Ethereum.
However, the approval of spot BTC ETFs and the increasing interest in Bitcoin could lead to significant growth in its ecosystem. This article explores the challenges and potential strategies for developing the Bitcoin ecosystem, with a focus on Layer 2 solutions.
2. Challenges and potential
Bitcoin faces challenges related to scalability, transaction speed, and fees, which limit its transaction processing capacity and hinder comprehensive DeFi support. The network consists of miners, nodes, stakeholders, developers, and a growing ecosystem that includes Layer 2 solutions, sidechains, and DApps.
- Mining tools and nodes validate transactions and maintain consensus through the Proof of Work consensus mechanism. However, this mechanism slows down the ecosystem’s growth compared to layer 1 which uses Proof of Stake.
- The developer community plays a crucial role in expanding the core ecosystem but faces challenges in achieving consensus on upgrades. The infrequent updates have led to scalability and programmability issues for Bitcoin.
To create a DApp ecosystem, scalable expansion solutions with smart contract capabilities, such as Layer 2 networks and sidechains, are essential. These solutions are crucial in creating favorable conditions for Bitcoin’s native ecosystem.
3. Bitcoin Layer 2s
3.1. Overview
The scaling solutions are protocols built on top of the blockchain base layer, designed to enhance its efficiency by processing transactions off the main blockchain. By handling off-chain transactions, they provide improved scalability, reduced transaction costs, and faster confirmation times. In addition to scalability, Layer 2 and sidechains can also introduce functionalities such as complex smart contract capabilities.
The first scaling solution to appear on the Bitcoin network is the Lightning Network. This platform is specifically designed to increase the speed and reduce the costs associated with transactions on the Bitcoin network. While Lightning Network performs well in this task and has attracted a significant total value locked (TVL) of over $275 million (according to DeFiLlama), it has not provided the necessary smart contract capabilities to form a complex native ecosystem of DApps.
Therefore, several other scaling solutions have emerged, specifically designed to enable smart contracts. Some of these solutions include:
- Stack: Stack functions as a smart contract and DApp layer for Bitcoin with its own blockchain using Proof of Transfer (PoT). This mechanism leverages Bitcoin’s PoW for security. It enhances Bitcoin’s functionality with DApps, DeFi, and a growing ecosystem.
- Rootstock/RSK: It is a Bitcoin sidechain that operates with full Turing-complete smart contracts and EVM compatibility. It uses the native RBTC coin with a fixed exchange rate of 1:1 with Bitcoin through a two-way peg. Projects like Sovryn and Money On Chain operate on RSK.
- Liquid Network: It is a Bitcoin sidechain developed by Blockstream with its native token LBTC, using a two-way peg mechanism. It provides tools for non-custodial trading, asset issuance, and confidential transactions. Liquid supports the creation of various digital assets such as NFTs, stablecoins, and tokens.
- Mintlayer: It is a Bitcoin sidechain that uses the Dynamic Slot Allocation (DSA) consensus mechanism, combining Bitcoin’s PoS and PoW. It supports smart contracts, asset issuance, and compatibility with the Lightning Network. The Mintlayer protocol also allows for cross-chain block transfers and peg-in/peg-out capabilities.
- RGB: RGB is an off-chain smart contract layer for Bitcoin, enabling the creation of digital assets such as tokens and NFTs. It uses Bitcoin’s UTXOs as single-use seals and provides full compatibility with the Lightning Network, ensuring fast settlement and scalability.
- Omni Layer: It is an asset platform and smart contract layer for Bitcoin, allowing token issuance and DEX. Tether (USDT) was initially launched on Omni. Omni Bolt, its upgrade, adds compatibility with the Lightning Network, enabling faster and more scalable Omni token transactions.
3.2. Stacks – notable project
The Bitcoin L2 project was initiated in 2017 to enable smart contracts for Bitcoin. The Stacks Network launched in January 2021, allowing smart contracts and decentralized applications to use Bitcoin as a secure L1. Stacks Bitcoin L2 activates the Bitcoin economy with its PoX consensus mechanism.
Stacks is currently the best L2 in terms of total value locked, developer activity, and other key metrics.
- TVL: $121 million
- Marketcap: Ranked in the top 35 out of 100
- Developer Activity: Continues to remain high.
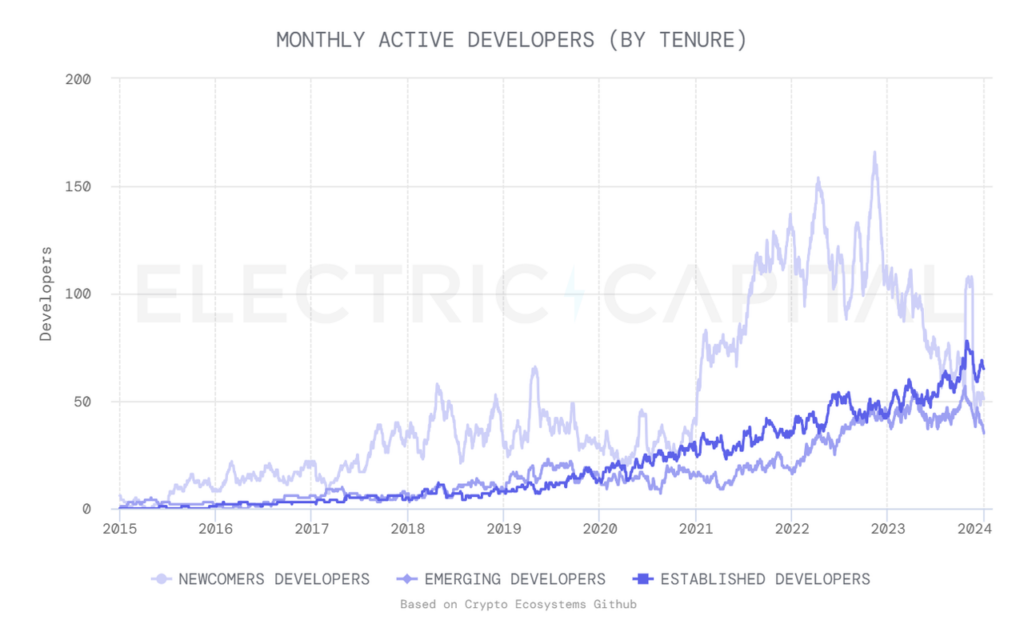
The Bitcoin ecosystem is ready for significant breakthroughs in the medium term, mainly driven by advances in L2 technologies such as the Stacks’ Nakamoto Release and the emergence of sBTC. These developments not only represent an increase but also a transformative change, particularly in the Bitcoin DeFi space and other applications.
- Significantly reducing block creation time (from over 10 minutes to 5 seconds) and enhancing security serve as tools to create a smooth user experience, ‘similar to Ethereum,’ which is crucial to attract new developers and catalyze a cycle of adoption and innovation. -> by decoupling Stacks blocks from Bitcoin blocks so that a Stacks miner can produce multiple blocks within one tenure.

- The deployment of fast blocks and sBTC will enable Stacks to offer high-value BTC-denominated applications, such as the NFT market, facilitating more efficient trading of unique L2 NFT collections and OrderBooks. The Bitcoin DeFi landscape is expected to undergo significant expansion, including lending and borrowing, which can be achieved with sBTC.
- Furthermore, in the upcoming Nakamoto upgrade, Stacks will introduce new subnets that support multiple programming languages and different execution environments, including EVM and Rust VM subnets. This significantly enhances the interaction capabilities of the Bitcoin ecosystem with other L2 blockchain networks.
With the successful completion of the “Instantiation” step of the Nakamoto upgrade on April 16, the next significant milestone is the “Activation” phase, which is scheduled for August 28.
4. Final Thoughts
The approval of a spot Bitcoin ETF is a significant milestone, marking the active involvement of major financial institutions such as BlackRock, VanEck, Fidelity, and others. This also serves as a catalyst for increasing demand for BTC-based trading products and profits due to the security, decentralization, and efficiency of Bitcoin itself.
Bitcoin’s Layer 2 solutions, although still in the early stages of development, are ready for significant growth. Particularly with the release of Stacks’ Nakamoto and the emergence of sBTC, they promise to revolutionize the DeFi landscape. These developments are expected to create a smoother and more efficient user experience and open up new possibilities for the NFT market and Bitcoin-based DeFi applications.
The information provided in this article is for reference only and should not be taken as investment advice. All investment decisions should be based on thorough research and personal evaluation.





