The horse racing industry has a long history spanning thousands of years, starting from ancient times when kings, nobles, and warriors employed horses for transportation, activities, and battlefields. Today, this industry has become a large-scale global business. From weekly races at local tracks to grand international events like the Kentucky Derby and Royal Ascot, people from all over the world flock to witness thrilling races and renowned thoroughbred racehorses.
The horse racing industry not only provides exciting races but also creates numerous business opportunities and employment. From horse training, and healthcare, to the construction and management of racing facilities, this industry has generated stable income for thousands of people.
Although the horse racing industry often faces challenges and controversies, there are ongoing efforts to ensure its sustainability and development. In this context, blockchain technology, with its applications in ensuring transparency and easy management, can be seen as a promising technological solution to address long-standing issues in the traditional horse racing industry. This can help develop or expand new business models, bringing added value to the horse racing industry.
In this article, the writer will study and analyze business models in the horse racing industry, and propose directions in which blockchain technology can contribute to the development and expansion of these models.
Horse Racing – A Billion-Dollar Industry
- The horse racing industry has become a significant part of the global economy, with an estimated market value of over $400 billion. In countries like the United States and the United Kingdom, the industry holds a notable position in their respective GDPs, contributing 0.5% of the US GDP and 0.3% of the UK GDP.
- The industry’s compound annual growth rate (CAGR) is projected to be 8.89% during the period from 2023 to 2030. Despite its long existence, the horse racing industry continues to experience continuous growth.
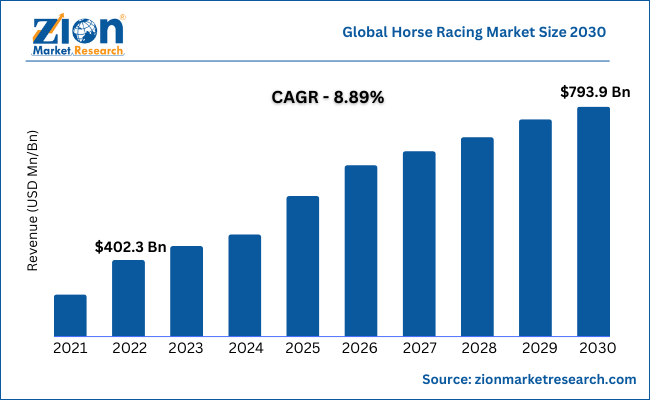
- In addition to providing employment opportunities for horse breeders, trainers, and managers, this industry generates income, wages, and other ancillary benefits worth $38 billion for related sectors.
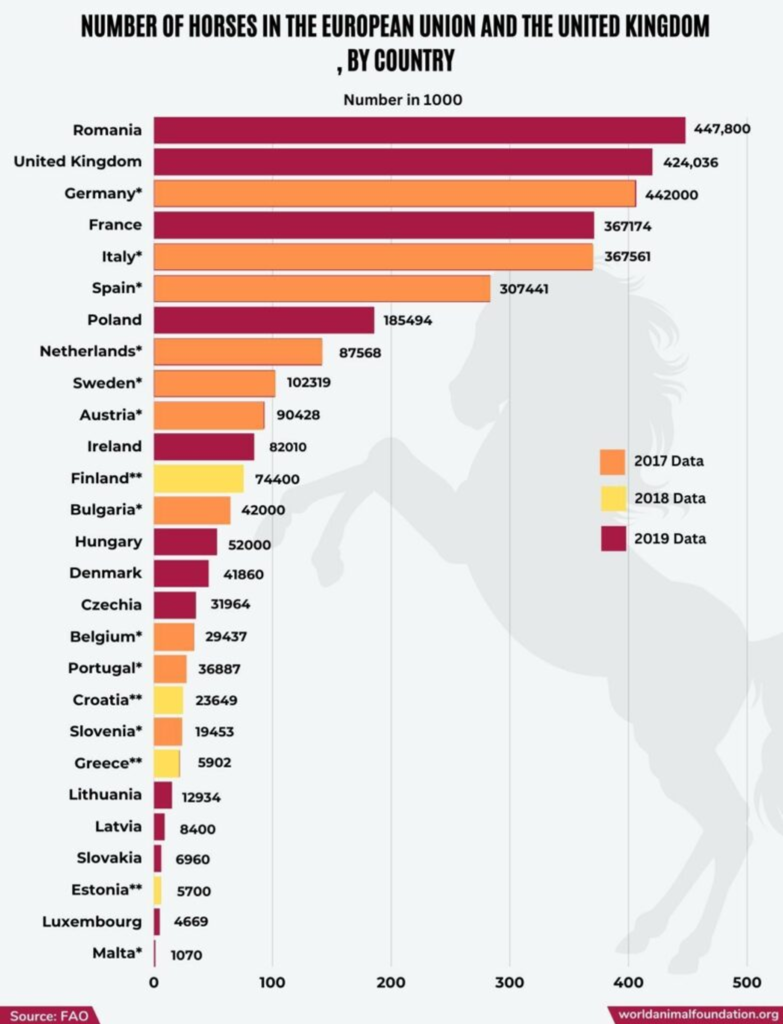
- In terms of horse population, the United States has the highest number of racehorses, with 1.2 million horses serving the horse racing industry. Following closely are the European Union countries and the United Kingdom.
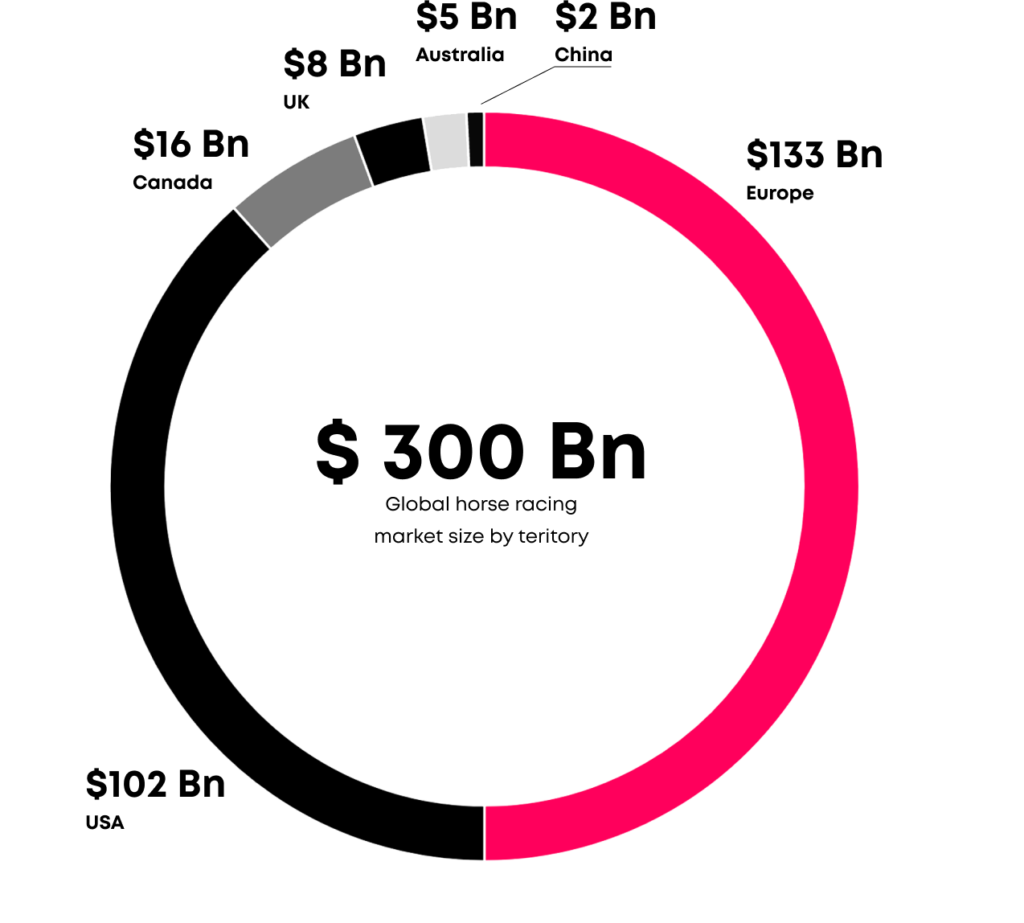
- In terms of market share:
- The United States and EU countries are the two regions that hold the largest market share in the global horse racing industry, accounting for over 80% of the market. Additionally, Australia, Canada, the United Kingdom, and Dubai also have thriving horse racing industries with significant development.
- In Asia, although there hasn’t been a significant market presence and horse racing betting is still considered illegal in most countries in the region, the trend shows an increasing demand for the sport among people in Asian countries, particularly in China and Japan.
- Most racehorses of the China Horse Club (CHC), the largest thoroughbred racing organization in China, were exported out of China before the ban on racing was lifted in 2011. However, certain regions in China have started promoting the sport, hoping to revitalize the domestic horse racing industry. Macau and Hong Kong are notable regions with thriving horse racing industries.
- In Japan, horse racing is one of the four sports (horse racing, bicycle racing, powerboat racing, and asphalt motorcycle racing) that are allowed for betting under special legislation and regulated by local governments or government-affiliated companies. Japan ranks second in global horse racing market share, following the United States and preceding Australia, according to data from Zion Market Research.
- Furthermore, horse racing is considered a comprehensive sport as the participants in a race can include men, women, children, and people with disabilities, spanning from 18 to 70 years of age. The age group above 45 years old has a higher participation rate in horse riding compared to other sports.
Not limited to racecourses
Taking advantage of the special appeal of racehorses to the interest and affection of fans, the horse racing industry has created many unique and highly profitable business models. Here are some popular business models alongside the traditional horse racing model:
- Racehorse farm ownership and management (Equine market):
- This model involves purchasing and owning racehorses and building and managing racehorse farms. The farm can provide services such as care, training, and the option for owners or racing teams to lease racehorses. It can even be combined with resorts and entertainment centers to offer combined tourism experiences. There are three main types of farms based on scale: small farms, racehorse centers, and racehorse villages. Interested readers can find more information here.
- This model requires significant capital investment to purchase land, build infrastructure, and buy racehorses. A farm may include horse stables, training areas, tracks, racecourses, and areas for horse care and medical treatment.
- Business models: partnering with hotel brands, restaurants, and resorts to create horse racing tourism destinations; leasing farms and facilities, leasing racehorses, renting event venues; organizing events.
- Establishing a racing team:
- This model involves establishing and managing a professional racing team (including horses and trainers) focused on owning and managing a group of racehorses to participate in races and achieve victories.
- This model requires high commitment, specialized knowledge of racehorses, and financial management skills. Understanding the horse racing industry, monitoring trends and changes in the field, and applying appropriate strategies are crucial for success.
- Business models: prize money for winning racehorses; selling merchandise and providing fan services for fan clubs; sponsorship contracts; training and care services for racehorses owned by others; stud fees for successful racehorses in major races.
- Commercializing racehorse ownership:
- This model involves buying and selling racehorses. Horse traders can purchase horses from farms or at horse racing auctions and then resell them to other owners or racing teams. They can also provide consulting services for horse purchases to clients.
- However, the percentage of horse owners in countries is not high (only about 0.3% of the population in the UK own horses, with the majority of horses belonging to the British royal family). Horse ownership requires a significant amount of time, space, and income, making it inaccessible to the majority of the population. To meet the increasing demand, a new business model called racehorse syndicate has emerged, allowing small investors to participate in the racehorse ownership experience with a small capital investment without the need for horse care and training responsibilities.
- Business models: horse auctions; selling racehorse ownership, fractional ownership – racehorse syndicates; horse purchasing consulting.
- Horse care and training services:
- This model focuses on providing care, training, and medical treatment services for racehorses. Governments and commercial organizations are investing in developing infrastructure for animal healthcare services since the pandemic highlighted the ease of disease transmission from animals to humans (in September 2021, the US Department of Agriculture invested $3 billion in animal health and nutrition).
- Business models: daily care and nutrition services; training and conditioning services; and specialized medical treatment services.
- Other supporting services in the horse racing industry:
- There are numerous business opportunities in supporting services within the horse racing industry.
- Business models: veterinary services; logistics services; marketing and advertising services; horse transportation services; and fan cooperative services.
- Betting and entertainment:
- This model involves providing online or in-person betting and entertainment services for the horse racing industry. Betting and casino companies often offer direct betting opportunities on horse races and organize horse racing-related entertainment events.
- However, the majority of Asian countries prohibit horse racing betting due to the lack of comprehensive legal frameworks for these types of activities.
- Business models: horse racing betting; live race streaming services.
- Bloodstock Market:
- The bloodstock market is a crucial business model in the racing industry, where stallions and mares are bred together to produce offspring with similar physical characteristics. This model plays a significant role in the development and improvement of racehorse breeds, aiming to create horses capable of performing well in races.
- Business models in the bloodstock market include breeding fees, breeding services, and breeding consultancy, as well as breeding insurance.
Barriers to Entry in the Horse Racing Industry
- For Fans or Investors:
- Restricted access to and limited information on racehorses: Sometimes, fans may face difficulties in accessing information and news about racehorses, racing events, and related information. This could be due to limited access to reliable sources of information or a lack of up-to-date and widely disseminated information.
- Geographical and legal barriers remain a challenging issue: Since horse racing is not a universally popular sport like football, some fans in countries wanting to experience the excitement of racecourses or own horses face barriers due to geographical distances and legal issues in their residing countries.
- Investing in horses is not a lucrative investment for small investors: The high cost of purchasing horses often leads small investors to seek solutions such as racehorse syndicates, as mentioned. However, most ownership rights from syndicates do not yield high profits. Legally, owning a share of a racehorse is not direct ownership, so participants in syndicates mostly pay for the emotional experience. This article will address this issue more specifically in the case study analysis below.
- For Businesses:
- Financial challenges: Operating in the horse racing industry requires substantial investment in infrastructure, horse care, training, and advertising. This can pose significant financial barriers to new and small businesses. The challenge is to leverage available services to apply them to their business models effectively.
- Regulation and legal issues: The horse racing industry is often subject to numerous regulations and laws related to organizing racing events, betting, horse care, and related business activities.
Blockchain – A Modern Technological Solution for the Traditional Horse Racing Market
In essence, blockchain technology has the following characteristics and applications:
- Trustworthiness: Blockchain is built on the principles of decentralization and public ledger, enhancing trustworthiness and transparency. All information recorded on the blockchain cannot be changed or removed, creating a reliable foundation for data tracking and verification.
- Secure and convenient transactions: Blockchain enables direct transactions between parties without the need for traditional intermediaries. This reduces costs and time while increasing security and safety for transactions in the industry.
Here are some directions and methods in which blockchain technology can be applied to the horse racing industry:
- Information management support: Use blockchain to help relevant parties track information about horse racing, including breeding, training, ownership, and racing history. This enhances transparency and trustworthiness in the industry.
- Fractional ownership management: For tracking horse ownership and recording ownership rights, blockchain can provide a system of decentralization and accurate authentication. Each horse can be linked to a unique identifier on the blockchain, allowing transparent tracking of ownership and ownership history that cannot be altered.
- Medical and genetic records: Blockchain can be used to store medical information and genetic traits related to racehorses. This enables owners and veterinarians to access and share information securely and efficiently.
- Transactions and payments: Blockchain can create a secure and transparent payment system in the horse racing industry. Transactions related to horse sales, training services, race winnings, and sponsorship contracts can be executed through smart contracts on the blockchain.
- Origin tracking and supply chain: Blockchain can be used to track and verify the origin of racehorses from the breeding, nurturing, and training processes to racing events. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of information about racehorses.
In conclusion, by applying blockchain technology, the horse racing industry can achieve greater transparency, safety, and efficiency in management, transactions, and horse care.
Case study: Racehorse fractional ownership
To gain a better understanding of how blockchain technology is applied in the horse racing industry, this article examines a case study on fractional ownership through racehorse syndicates—a fascinating business model that can leverage blockchain technology.
“Democratizing” Racehorse Ownership
- Racehorse ownership was traditionally considered a privilege reserved for a small group or royalty. However, with the emergence of syndicates, this exciting experience has become more “democratized.” A racehorse syndicate is a group of individuals who share the “ownership” or “financial benefits” of a racehorse, known as “fractional ownership.” When participating in a syndicate, members not only receive financial benefits but also have the opportunity to interact closely with the horse and even have voting rights on important matters such as naming the horse or breeding decisions. Therefore, when deciding to join a syndicate, it is important to understand the benefit distribution of the organization.
- Many racehorse syndicate companies are often organized as Limited Liability Companies (LLCs). The LLC model offers several benefits and flexibility for racehorse syndicate companies:
- Personal asset protection: LLCs allow syndicate members (investors) to protect their personal assets from the company’s debts and legal liabilities.
- Flexible management: LLCs enable the use of a flexible management model, where members can organize and operate the company according to their own regulations and agreements. Members can decide on profit sharing, management authority, and other important issues within the syndicate.
- Capital recovery capability: With the LLC model, members can easily transfer or sell their shares. This creates flexibility and the ability to restructure the syndicate in the event of changes in members or investment needs.
- Information technology and social networks have created a favorable environment for promoting and managing racehorse syndicates. Participants can share information, communicate, and manage horse ownership interactively through online platforms.
Ownership rights in horse racing, when divided into smaller shares, only provide emotional experiences.
Online syndicates like CommonWealth and myRacehorse have emphasized through their media channels that investing in fractional ownership of racehorses is a risky investment. They believe that investors should maintain a mindset that investing in racehorses means focusing on the experience, and predicting how well a horse will perform on the racetrack is unpredictable.
- The value of a racehorse lies in several factors, including prize money from races, stud fees, insurance, and the emotional benefits that owners receive from participating in horse racing activities.
- In most cases, shareholders of a specific racehorse only benefit from prize money and experiential benefits. However, the winning rate among thousands of racehorses is very low, while the actual economic value comes from stud fees and sponsorship contracts, especially if the horse gains a reputation on the racetrack. Syndicates often do not distribute all these benefits to the owners, as they need to ensure cash flow in their financial plans, and when all the rights are transferred to the owners, they lose the motivation to nurture and train horses in the future.
- Looking deeper into cost considerations, the price of a specialized thoroughbred racehorse can range from $200,000 to $400,000, not to mention the costs of care and training, which can reach up to $50,000 per year. Therefore, syndicates frequently make capital calls for members.
- Additionally, when risks such as horse injuries or losses occur, investors do not receive any compensation.
- Another challenge for traditional syndicate models is the low liquidity of racehorse shares.
Applying blockchain technology to enhance user and investor experiences
It can be seen that, as mentioned by the syndicate companies, investing in racehorse ownership is not a lucrative financial investment. Blockchain is one of the solutions that can innovate this business model.
- Blockchain helps reduce fraud and facilitate efficient transactions:
- Using blockchain technology and smart contracts to manage the fractional ownership rights of racehorses. Each ownership element is recorded on the blockchain and verified through smart contracts. This ensures safety and transparency in ownership transfers.
- Enhancing liquidity and exit opportunities through NFTs. NFTs function as digital ownership certificates, allowing owners to trade their ownership rights through the blockchain. Compared to traditional stock markets, NFTs enable a more vibrant market that can trade 24/7, along with the ability to be proactive instead of relying on a third-party intermediary. This attracts more participants and capital to the market, creating additional revenue for businesses.
- Consequently, increasing benefits for investors: When businesses find ways to minimize costs and generate additional revenue by applying blockchain to their business models, they will consider providing more diverse benefits to investors. This creates a sustainable business model.
TL;DR
- The horse racing industry has become an important part of the global economy, with an estimated market value of over $400 billion. The CAGR of the horse racing industry is forecasted to be 8.89% during the period from 2023 to 2030.
- In terms of market share, the United States and EU countries account for over 80% of the global market. Additionally, Australia, Canada, the UK, and Dubai also have a strong presence in the horse racing industry. In Asia, China, Macau, Hong Kong, and Japan are emerging markets with more favorable legal signals.
- The business models in the horse racing industry include Ownership and management of racehorse farms, Formation of racing teams, Commercialization of racehorse ownership rights, Horse care and training services, Other supporting services in the horse racing industry, Betting and entertainment, Bloodstock market (breeding market).
- Blockchain can help improve the management process of information related to horse racing, ownership rights, and transactions, ensuring transparency and security in the market. It gradually realizes the vision of securitizing real assets, in this case, racehorse ownership.





