Ethereum is poised for a significant transformation with the introduction of the Beam Chain, a proposal aimed at overhauling its consensus layer. This initiative seeks to address the limitations of the current Beacon Chain, which has remained unchanged for five years. By integrating recent advancements in technology and research, Beam Chain promises to enhance Ethereum’s performance, security, and sustainability while maintaining compatibility with existing applications.

1. The Need for Redesign
The primary motivation behind the Beam Chain redesign is the aging of the Beacon Chain. Since its specifications were finalized five years ago, both technological advancements and our understanding of critical concepts such as Maximum Extractable Value (MEV) have evolved significantly. This evolution has highlighted the necessity for a more robust consensus mechanism capable of mitigating MEV’s adverse effects.
Moreover, breakthroughs in zero-knowledge-proof technologies, particularly SNARKs and ZKVM, have made it possible for non-experts to utilize these complex systems effectively. The redesign also presents an opportunity to address technical debt accumulated over the years, ensuring that Ethereum remains competitive and secure in a rapidly changing technological landscape.

2. Key Features of Beam Chain
The Beam Chain proposal focuses exclusively on the consensus layer while deliberately excluding the data and execution layers used by applications. This targeted approach allows for substantial improvements without disrupting existing functionalities.
The proposal outlines nine major enhancements categorized into three main areas:
- Block Production: This includes improving MEV handling, enhancing censorship resistance, introducing inclusion lists, achieving proposer-builder separation, and shortening slot times.
- Staking: Key changes involve correcting issuance curves, reducing the minimum validator stake from 32 ETH to 1 ETH, and achieving single-slot finality.
- Cryptography: The implementation of real-time SNARKing and post-quantum secure cryptographic schemes will bolster security.
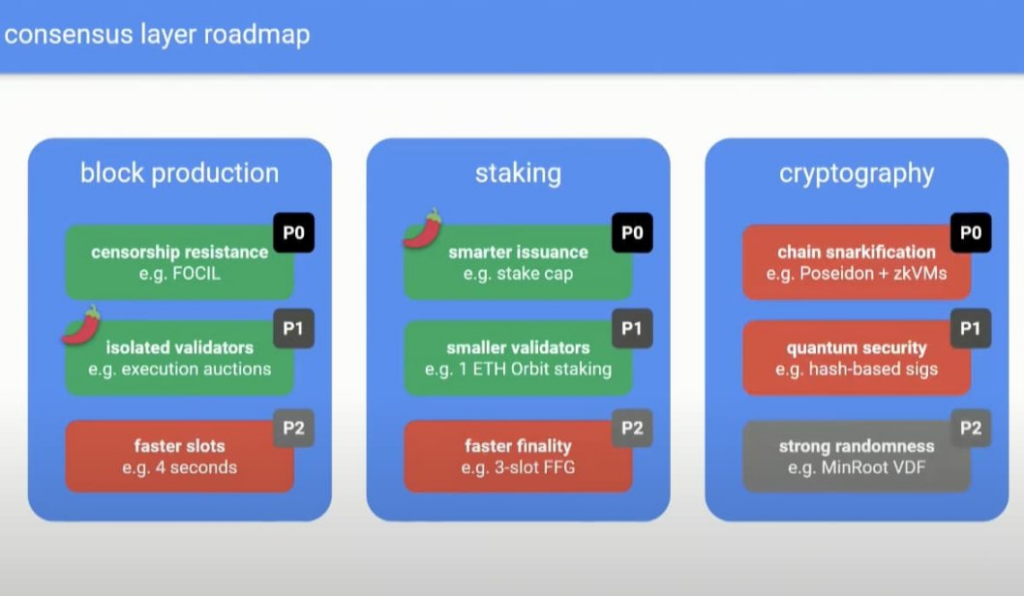
By executing these upgrades simultaneously—termed “accelerated ossification”—the Ethereum network can transition into maintenance mode more swiftly, thereby reducing long-term uncertainty.
3. Challenges Ahead
Despite its ambitious goals, the Beam Chain proposal faces several challenges that must be navigated carefully:
- Technical Complexity: Integrating real-time SNARKing and post-quantum cryptography introduces substantial technical hurdles. Changes to hash functions, signature schemes, and state serialization methods are necessary to implement these features effectively.
- Risk Management: The simultaneous implementation of multiple major changes heightens systemic risk. Rigorous testing and validation processes will be essential to ensure network security during this transition.
- Community Consensus: Achieving broad community support is crucial for the proposal’s success. Coordination among various client teams will be necessary to onboard new technologies effectively.
- Timeline Delays: Given the complexity of these upgrades, there may be delays in implementation. Flexibility and contingency plans will be vital to address potential setbacks.
- Standardization: Ensuring compatibility across diverse ZKVM implementations is crucial to avoid fragmentation within the ecosystem. A ZKVM-agnostic approach will help mitigate complexity.
- Long-Term Security: New technologies must be integrated without introducing vulnerabilities that could compromise Ethereum’s long-term stability.
Extensive testing over several years will be required to safely deploy these new technologies on the main net.
4. Clarifying Misconceptions About Layer 2
Recent rumors have suggested that the Beam Chain upgrade poses a threat to layer 2 solutions within the Ethereum ecosystem. However, this notion is unfounded and has caused unnecessary concern among developers and users alike.
Firstly, it is essential to clarify that Beam Chain is not a new chain or token issuance; rather, it is an upgrade to the existing Beacon Chain that aligns with Ethereum’s established roadmap. The integration of an inclusion list in block production aims to enhance transaction order integrity while preserving layer 2’s role in managing user applications and traffic.
Secondly, while Beam Chain will improve mainnet scalability through SNARKs—shifting from validating all data to validating proofs—this enhancement does not diminish layer 2’s functionality. Instead, it complements layer 2 solutions by potentially allowing standout projects to transition directly onto the mainnet through a modular approach with alt-VMs.
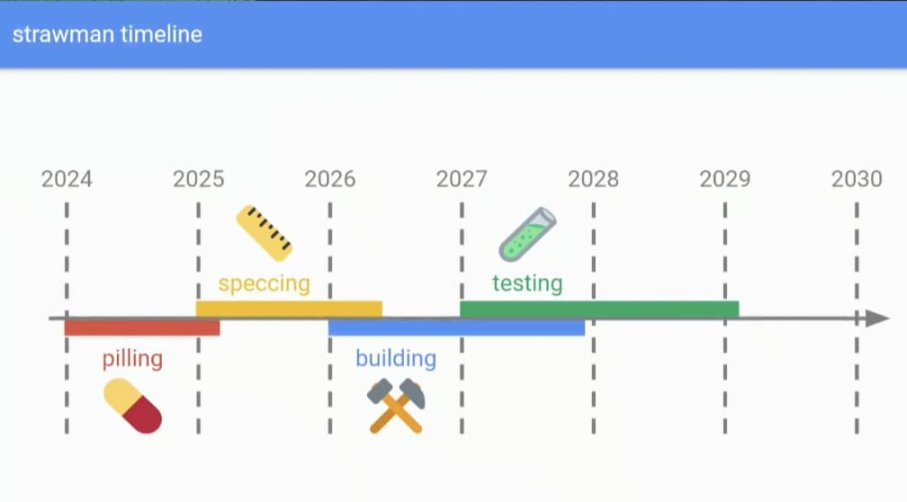
In conclusion, as Ethereum embarks on this transformative journey with Beam Chain, it is crucial for stakeholders to focus on collaboration and innovation rather than succumbing to fear-based narratives. The upcoming era of zero-knowledge rollups promises significant advancements for both Ethereum’s main net and its layer 2 solutions, setting the stage for a more scalable and resilient blockchain ecosystem.
The information provided in this article is for reference only and should not be taken as investment advice. All investment decisions should be based on thorough research and personal evaluation.





